Letter Coding Decoding




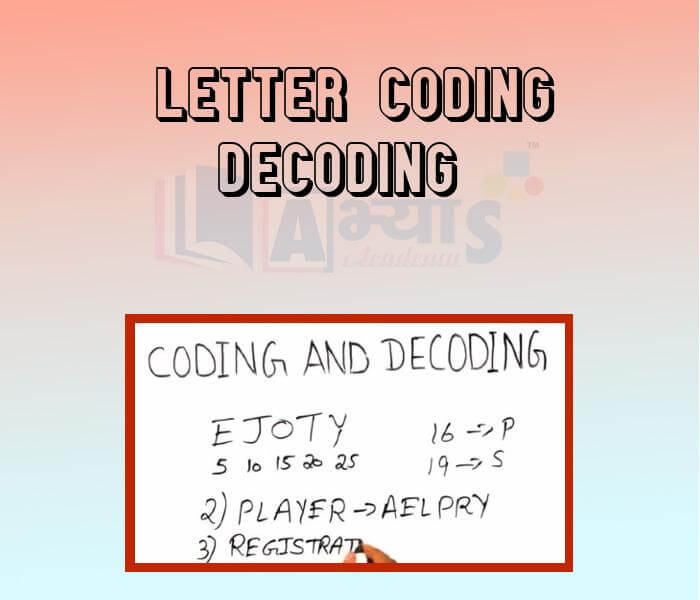
Letter Coding Decoding
Letter Coding Decoding:
Introduction:
For conveying secret messages from one place tp another , especially in Defence Services, coding is used. The codes are based on various principles/patterns such that the message can be easily be deciphered at the other end. Now-a-days, in certain competitive examinations, such questions are given to judge the candidates intelligence and mental ability. They are required to encode and decode words and sentences after observing the pattern and principles involved. It is always easy to handle numbers than alphabet letters. So, if there is a set of questions on alphabet coding in the exam, it is better to use this table to decipher the code.
Left to Right
A-1 | B-2 | C-3 | D-4 | E-5 | F-6 | G-7 | H-8 | I-9 | J-10 | K-11 | L-12 | M-13 |
N-14 | O-15 | P-16 | Q-17 | R-18 | S-19 | T-20 | U-21 | V-22 | W-23 | X-24 | Y-25 | Z-26 |
To Remember !
E-5 | J-10 | O-15 | T-20 | Y-25 |
C-3 | F-6 | I-9 | L-12 | O-15 | R-18 | U-21 | X-24 |
Right to Left
Z-1 | Y-2 | X-3 | W-4 | V-5 | U-6 | T-7 | S-8 | R-9 | Q-10 | P-11 | O-12 | N-13 |
M-14 | L-15 | K-16 | J-17 | I-18 | H-19 | G-20 | F-21 | E-22 | D-23 | C-24 | B-25 | A-26 |
To Remember !
B-25 | G-20 | L-15 | Q-10 | V-5 |
C-24 | F-21 | I-18 | L-15 | O-12 | R-9 | U-6 | X-3 |
Series of Opposite Alphabets
A-Z | B-Y | C-X | D-W | E-V | F-U | G-T |
H-S | I-R | J-Q | K-P | L-O | M-N |
Sum of the positional numbers of opposite letters in the alphabet is always 27.
TYPE 1:TYPE 2:
Letter Coding on Specific Pattern
In such questions, letters of alphabets are no doubt allotted artificial values but based on certain specific patterns/priciples. The candidates are required to first observe the specific pattern involved and then prceed with coding or decoding as the case may be.
Example 1 If POSTED is coded as DETSOP, how will be word SPEED be coded?
Solution A careful observation of the above example will reveal that letters of the first word have been reversed
fig. required
Similarly,
fig. required
Example 2 If A = E, how will you code the following words?
(1) BLACK (2) ACT (3) BAT (4) CADRE (5) LOOT
(6) FOOL
Solution (1) FPEGO (2) EGX (3) FEX (4) GEHVI (5) PSSX
(6) JSSP
Example 3 If CAT is coded as DEBCUV , how will you code RACE ?
SOlution The pattern of coding is such that each letter has been allotted value of 2 letters following the sequence, i.e. A = BC, B = CD, C = DE, etc.
Hence, the word RACE will be coded as STBCDEFG
BASED on the above principle, try to code the following.
(1) FATHER (2) DATED (3) LATE (4) FAKES (5) MAIN (6) PLANE
Solution (1) G H B C U V I J F G S T (2) E F B C U V F G E F
(3) M N B C U V F G (4) G H B C L M F G T U
(5) N O B C J K O P (6) Q R M N B C O P F G
Example 4 If EGHJKMKM is the code for FILL, how will you decode the following?
(1) QSDFRTSU (2) SUDFKMKM (3) EGDFDFKM
(4) CENPDFRT (5) KMNPRTSU (6) ACDFCERT
Solution The pattern of coding is such that the sequence follows the letters in between. each pair of letters in the code.
Pattern is AC = B, BD= C, CE = D, etc.
(1) REST (2) TELL (3) FEEL
(4) DOES (5) LOST (6) BEDS
TYPE 3:
Miscellaneous Types
Decoding the Rule Applied
This part of coding test required a careful examination of rules followd to code a certain word. Only after the analysis of the pattern applied in coding, you can decode them.
Example
Study the five different ways of coding marked (1), (2), (3), (4) & (5). A specific rule has been applied to codify each of them. Can you find out the rule of coding applied in the question that follows.
F R A N C E = (1) N C E F R A
(2) F A C R N E
(3) E C N A R F
(4) A C E F N R
(5) F E R C A N
WORD CODE
1. C A N A D A C N D A A A
2. K E N Y A K A E Y N
3. N A T I O N S S N O I T A N
4. V A N D A N A V N A A A D N
5. V A R D H M A N N A M H D R A V
6. V A R I O U S A I O R S U V
7. C A R E E R E E R C A R
8. P O P U L A T I O N P N O O P I U T L A
9. M E D I C I N E M D C N E I I E
10. A P T I T U D E A D E I P T T U
Answers:
1. ( 2) 2. (5) 3. (3) 4. (2) 5. (3) 6.(4) 7.(1) 8. (5) 9. (2) 10.(4)
Explanations
The rules by which the different pattern of coding is made are as follows.
(1) The former part (FRA) gets transferred after the latter part (NCE). The coding is made in the order given below:
image required
(2) The pattern is that every letters gets transferred on the adjacent line of the code.
image required
(3) The sequence is the backward rearrangement of letter.
image required
(4) The sequence is the rearrangement of letters with respect to the order of regular of alphabets.
image required
(5) The first and the last letters are made the first two letters in the code the second and the fifth letter are made the third and fourth letters in the code the third and the fourth letters are made the last two letters respectively.
image required
TYPE 4:
Contrasting and Making Comparisons
A set of words are given in column I and codes have been formed in column II. Here in such questions some alphabets/letter are underline in column I and the corresponding codes in column II has been jumbled up thus making the question more difficult to correspond. To find the formula to decode these type of question some logical rule/priciple is found by comparing or making contracts in all the questions. An example has been given below:
Example
In the following question the capital letters in column I are codified in small letters in column II. The small letters are not arranged in the same order on the capital letters. Study the column (I) and (II) together and determine the small letters for the corresponding underlined capital letter in column (I).
Column (I) Column (II)
1. D I G I T w b z b m
2. T I G E R m b z x k
3. F E V E R x k y o x
4. G I T A R m t z b k
5. L I V E R b e x o k
Keys: 1. w 2. m 3. y 4. z 5. e
Explanation:
If we compare question (1) & (2) we find that there are 3 alphabets (T, I, G)
Letter Coding Decoding:
Introduction:
For conveying secret messages from one place to another , especially in Defence Services, coding is used. The codes are based on various principles/patterns such that the message can be easily be deciphered at the other end. Now-a-days, in certain competitive examinations, such questions are given to judge the candidates intelligence and mental ability. They are required to encode and decode words and sentences after observing the pattern and principles involved. It is always easy to handle numbers than alphabet letters. So, if there is a set of questions on alphabet coding in the exam, it is better to use this table to decipher the code.
Left to Right
A 1 | B 2 | C 3 | D 4 | E 5 | F 6 | G 7 | H 8 | I 9 | J 10 | K 11 | L 12 | M 13 |
N 14 | O 15 | P 16 | Q 17 | R 18 | S 19 | T 20 | U 21 | V 22 | W 23 | X 24 | Y 25 | Z 26 |
To Remember !
E 5 | J 10 | O 15 | T 20 | Y 25 |
C 3 | F 6 | I 9 | L 12 | O 15 | R 18 | U 21 | X 24 |
Right to Left
Z 1 | Y 2 | X 3 | W 4 | V 5 | U 6 | T 7 | S 8 | R 9 | Q 10 | P 11 | O 12 | N 13 |
M 14 | L 15 | K 16 | J 17 | I 18 | H 19 | G 20 | F 21 | E 22 | D 23 | C 24 | B 25 | A 26 |
To Remember !
B 25 | G 20 | L 15 | Q 10 | V 5 |
C- 24 | F- 21 | I-18 | L-15 | O-12 | R-9 | U-6 | X-3 |
Series of Opposite Alphabets
A Z | B Y | C X | D W | E V | F U | G T |
H S | I R | J Q | K P | L O | M N |
Sum of the positional numbers of opposite letters in the alphabet is always 27.
TYPE 1:
Coding with Letters of Alphabet
In these questions, the letters of the alphabets are exclusively used. These letters do not stand for themselves but are alloted some artificial values based on some logical patters/analogies. By applying those principles or observing the patterns involved, the candidates are required to decode a coded words. These can be further classified into the following categories:
SImple Analogical Letter Coding
These are also called arbitrary codes. There are 2 definite principles/pattern involved. Codes are based on the analogy of one example from which different codes are to be formed.
Example 1: If NETWORK is coded as O P C T R S Q, what can be coded as CROPS?
Solution N = O C = T
E = P R = O
T = C then O = N
W = T P = E
O = R S = R
R = S
K = Q
Hence CROPS can be coded as TONER.
Example 2: If INLAND is coded as BSTRSI, make codes of the following letters.
(1) IN (2) LAND (3) INN (4) AND (5) AN
(6) LAID
Solution The coding is done as follows:
(1) BS (2) TRSI (3) BSS (4) RSI (5) RS
(6) TRBI
Example 3: If SWFGHONTISO stands for OBSERVATION, code the following letters.
(1) RATION (2) RATE (3) SEAT (4) NOT (5) NOTE
(6) BEST
Soltuon The coding is as follows:
(1) HNTISO (2) HNTG (3) PGNT (4) OST (5) OSTG
(6) WGFT
Example 4: Column A contains certain words numbered from (1) to (6). Column B goes with the codes for column A, but with different order. You have to match the words of column A with their respective coded word in column B. The pattern of coding used here is BLADES = CMBEFT.
Column (A) Column (B)
(1) BASE (1) CBE
(2) BALE (2) CBTF
(3) SALE (3) CFE
(4) SAD (4) CBMF
(5) BAD (5) TBE
(6) BED (6) TBMF
Solution A(1) B(2), A(2) B (4), A(3) B (6), A(4) B(5), A(5) B(1), A(6) B(3).
TYPE 2:
Letter Coding on Specific Pattern
In such questions, letters of alphabets are no doubt allotted artificial values but based on certain specific patterns/priciples. The candidates are required to first observe the specific pattern involved and then prceed with coding or decoding as the case may be.
Example 1 If POSTED is coded as DETSOP, how will be word SPEED be coded?
Solution A careful observation of the above example will reveal that letters of the first word have been reversed
fig. required
Similarly,
fig. required
Example 2 If A = E, how will you code the following words?
(1) BLACK (2) ACT (3) BAT (4) CADRE (5) LOOT (6) FOOL
Solution:
Solution (1) FPEGO (2) EGX (3) FEX (4) GEHVI (5) PSSX (6) JSSP
Example 3 If CAT is coded as DEBCUV , how will you code RACE ?
SOlution The pattern of coding is such that each letter has been allotted value of 2 letters following the sequence, i.e. A = BC, B = CD, C = DE, etc.
Hence, the word RACE will be coded as STBCDEFG
BASED on the above principle, try to code the following.
(1) FATHER (2) DATED (3) LATE (4) FAKES (5) MAIN (6) PLANE
Solution (1) G H B C U V I J F G S T (2) E F B C U V F G E F
(3) M N B C U V F G (4) G H B C L M F G T U
(5) N O B C J K O P (6) Q R M N B C O P F G
Example 4 If EGHJKMKM is the code for FILL, how will you decode the following?
(1) QSDFRTSU (2) SUDFKMKM (3) EGDFDFKM
(4) CENPDFRT (5) KMNPRTSU (6) ACDFCERT
Solution The pattern of coding is such that the sequence follows the letters in between. each pair of letters in the code.
Pattern is AC = B, BD= C, CE = D, etc.
(1) REST (2) TELL (3) FEEL
(4) DOES (5) LOST (6) BEDS
TYPE 3:
Miscellaneous Types
Decoding the Rule Applied
This part of coding test required a careful examination of rules followed to code a certain word. Only after the analysis of the pattern applied in coding, you can decode them.
Example
Study the five different ways of coding marked (1), (2), (3), (4) & (5). A specific rule has been applied to codify each of them. Can you find out the rule of coding applied in the question that follows.
F R A N C E = (1) N C E F R A
(2) F A C R N E
(3) E C N A R F
(4) A C E F N R
(5) F E R C A N
WORD CODE
1. C A N A D A C N D A A A
2. K E N Y A K A E Y N
3. N A T I O N S S N O I T A N
4. V A N D A N A V N A A A D N
5. V A R D H M A N N A M H D R A V
6. V A R I O U S A I O R S U V
7. C A R E E R E E R C A R
8. P O P U L A T I O N P N O O P I U T L A
9. M E D I C I N E M D C N E I I E
10. A P T I T U D E A D E I P T T U
Answers:
1. ( 2) 2. (5) 3. (3) 4. (2) 5. (3) 6.(4) 7.(1) 8. (5) 9. (2) 10.(4)
Explanations
The rules by which the different pattern of coding is made are as follows.
(1) The former part (FRA) gets transferred after the latter part (NCE). The coding is made in the order given below:
image required
(2) The pattern is that every letters gets transferred on the adjacent line of the code.
image required
(3) The sequence is the backward rearrangement of letter.
image required
(4) The sequence is the rearrangement of letters with respect to the order of regular of alphabets.
image required
(5) The first and the last letters are made the first two letters in the code the second and the fifth letter are made the third and fourth letters in the code the third and the fourth letters are made the last two letters respectively.
image required
TYPE 4:
Contrasting and Making Comparisons
A set of words are given in column I and codes have been formed in column II. Here in such questions some alphabets/letter are underline in column I and the corresponding codes in column II has been jumbled up thus making the question more difficult to correspond. To find the formula to decode these type of question some logical rule/priciple is found by comparing or making contracts in all the questions. An examplehas been given below:
Example
In the following question the capital letters in column I are codified in small letters in column II. The small letters are not arranged in the same order on the capital letters. Study the column (I) and (II) together and determine the small letters for the corresponding underlined capital letter in column (I).
Column (I) Column (II)
1. D I G I T w b z b m
2. T I G E R m b z x k
3. F E V E R x k y o x
4. G I T A R m t z b k
5. L I V E R b e x o k
Keys: 1. w 2. m 3. y 4. z 5. e
Explanation:
If we compare question (1) & (2) we find that there are 3 alphabets (T, I, G) common and there corresponding small letters will be (m, z, b) though not in the same order. This leaves us with (D and R) with small alphabets (w and k). Therefore, we have now,
Either w or k is D s code
Now, if we taken (2) and (3), we find that w is not present is column II of either (2) or (3) and D is not there in column II of either (2) & (3) the or conclude that D = w and therefore R = k.
Now, carrying on with this finding, we see in question (3) and (5) there are two common elements in column I, V, E & R. Since E comes twice in (3), therefore code for E = x which leads to V = o and F =y in question is (1), I comes twice, this leads to I = b. So we are left with T and G which are either z or m.
Now, we cannot conclude anything more from these clues, but can fit in above observation to see what relation capital letters have with small letters.
A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | I | J | K | L | M | N | O | P | Q | R | S | T | U | V | W | X | Y | Z |
w | x | y | b | k | o | ||||||||||||||||||||
t | U | v | w | x | y | z | a | b | c | d | e | f | g | h | i | j | k | l | m | n | o | p | q | r | s |
Which word from the following canot be formed using the letters given in the word : EFFICIENT | |||
| Right Option : C | |||
| View Explanation | |||
Which word from the following canot be formed using the letters given in the word : PRESIDENTIAL | |||
| Right Option : A | |||
| View Explanation | |||
Which word from the following cannot be formed using the letters given in the word : PROSPECTIVE | |||
| Right Option : D | |||
| View Explanation | |||
Students / Parents Reviews [20]
One of the best institutes to develope a child interest in studies.Provides SST and English knowledge also unlike other institutes. Teachers are co operative and friendly online tests andPPT develope practical knowledge also.

Aman Kumar Shrivastava
10thAbhyas is good institution and a innovative institute also. It is a good platform of beginners.Due to Abhyas,he has got knoweledge about reasoning and confidence.My son has improved his vocabulary because of Abhyas.Teacher have very friendly atmosphere also.

Manish Kumar
10thAbhyas institute is one of the best coaching institute in the vicinity of Ambala cantt.The institute provides good and quality education to the students.The teachers are well experienced and are very helpful in solving the problems. The major advantages of the institute is extra classes for weak...

Shreya Shrivastava
8thMy experience with Abhyas academy is very nice or it can be said wonderful. I have been studying here from seven class. I have been completing my journey of three years. I am tinking that I should join Abhyas Academy in tenth class as I am seeing much improvement in Maths and English

Hridey Preet
9thA marvelous experience with Abhyas. I am glad to share that my ward has achieved more than enough at the Ambala ABHYAS centre. Years have passed on and more and more he has gained. May the centre flourish and develop day by day by the grace of God.

Archit Segal
7thIt was a good experience with Abhyas Academy. I even faced problems in starting but slowly and steadily overcomed. Especially reasoning classes helped me a lot.

Cheshta
10thIt was good as the experience because as we had come here we had been improved in a such envirnment created here.Extra is taught which is beneficial for future.

Eshan Arora
8thAbhyas institute is one of the best coaching institute in the vicinity of Ambala Cantt area. The teachers of the institute are well experienced and very helpful in solving the problems of the students.The good thing of the institute is that it is providing extra classes for the students who are w...

Aman Kumar Shrivastava
10thBeing a parent, I saw my daughter improvement in her studies by seeing a good result in all day to day compititive exam TMO, NSO, IEO etc and as well as studies. I have got a fruitful result from my daughter.

Prisha Gupta
8thMy experience was very good with Abhyas academy. I am studying here from 6th class and I am satisfied by its results in my life. I improved a lot here ahead of school syllabus.

Ayan Ghosh
8thIn terms of methodology I want to say that institute provides expert guidence and results oriented monitering supplements by requsite study material along with regular tests which help the students to improve their education skills.The techniques of providing education helps the students to asses...

Aman Kumar Shrivastava
10thThe experience was nice. I studied here for three years and saw a tremendous change in myself. I started liking subjects like English and SST which earlier I ran from. Extra knowledge gave me confidence to overcome competitive exams. One of the best institutes for secondary education.

Aman Kumar Shrivastava
10thIt has a great methodology. Students here can get analysis to their test quickly.We can learn easily through PPTs and the testing methods are good. We know that where we have to practice

Barkha Arora
10thMy experience with Abhyas academy is very good. I did not think that my every subject coming here will be so strong. The main thing is that the online tests had made me learn here more things.

Hiya Gupta
8thAbout Abhyas metholodology the teachers are very nice and hardworking toward students.The Centre Head Mrs Anu Sethi is also a brilliant teacher.Abhyas has taught me how to overcome problems and has always taken my doubts and suppoeted me.

Shreya Shrivastava
8thMy experience with Abhyas Academy has been very good. When I was not in Abhyas whenever teacher ask questions I could not speak it confidently but when I came in Abhyas, my speaking skills developed and now I am the first one to give the answer of teachers question.

Upmanyu Sharma
7thWe started with lot of hope that Abhyas will help in better understnding of complex topics of highers classes. we are not disappointed with the progress our child has made after attending Abhyas. Though need to mention that we expected a lot more. On a scale of 1-10, we would give may be 7.

Manya
8thAbhyas academy is great place to learn. I have learnt a lot here they have finished my fear of not answering.It has created a habit of self studying in me.The teachers here are very supportive and helpful. Earlier my maths and science was good but now it has been much better than before.

Barkha Arora
10thAbhyas Methodology is very good. It is based on according to student and each child manages accordingly to its properly. Methodology has improved the abilities of students to shine them in future.

Manish Kumar
10thI have spent a wonderful time in Abhyas academy. It has made my reasoning more apt, English more stronger and Maths an interesting subject for me. It has given me a habbit of self studying
